electrolysis consumption, and activated carbon filtration (or tank liquid treatment), regular supplementation must be carried out based on the results of the Hull tank test. Due to expiration and deterioration, organic additives have a significant impact on the quality of bright nickel plating.
2. Control of pH value, temperature, current density, and water quality. Under normal operating conditions, the pH value of bright nickel plating solution will increase with the progress of electroplating. Generally, adding acid will maintain the pH value within the predetermined process range. Add sulfuric acid to the electroplating solution based on Watt nickel solution to adjust the pH value; And adding amino sulfonic acid to the nickel plating solution to control the pH value. The operating temperature has a significant impact on the performance of the coating and should be maintained within the specified process range, with temperature fluctuations not exceeding ± 2 ℃. Usually, the temperature for most nickel plating processes is between 40-60 ℃. Controlling the cathodic current density is crucial for meeting the minimum coating thickness requirements, producing stable and consistent coatings, and achieving the expected performance. Because the current density determines the deposition rate, in order to obtain a uniform coating, the current density should be as uniform as possible. If necessary, a reasonable hanging device can be used and the workpiece on the hanging device can be placed in the appropriate position. Non conductor shielding and hanging plates can be used, and auxiliary anodes can be used to control the current distribution. Under careful operation and control, a bright nickel plating layer with uniform thickness can be obtained. The quality of the water used for tank preparation and the water used to supplement evaporation losses is very important, especially if the calcium concentration in tap water is high, which has a significant impact on the quality of the plating solution and thus affects the quality of the coating. Therefore, it is necessary to use distilled water and softened water. If conditions permit, filtering the water before adding it to the plating bath is an effective measure to eliminate the possibility of rough coating.
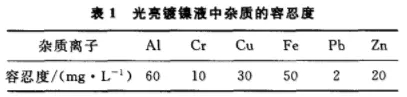
3. Control of Impurity Ions In daily operations, inorganic, organic, and gas impurities may be introduced into the plating solution. Efforts should be made to eliminate the root causes of these impurities in the plating workshop in order to improve the quality of the coating, production efficiency, and economic benefits. There are many reasons that lead to the increase of inorganic impurities, including the technical grade of the inorganic materials used, the carrying of hard water and acidic activation tanks, dust in the air, corrosion of metal heaters, corrosion of tank bodies at lining cracks, corrosion of anode rods, dust from equipment and buildings on the tank, and corrosion of parts and hangers that fall into the tank liquid and are not removed in a timely manner. When these inorganic impurity ions accumulate to a certain amount, the electroplating quality will plummet, and in severe cases, it will make production difficult to maintain. Table 1 shows the highest tolerance of inorganic metal impurities in bright nickel plating solution. Inorganic metal impurities have a significant impact on certain properties of the coating, therefore, they must be controlled. Low current density (0.2-0.5A/dm2) electrolysis and continuous filtration are usually used to control the pollution of most inorganic materials.
There are many reasons that lead to the increase of organic impurities, including: poor quality of organic additives and decomposition products, unclean surface pre-treatment cleaning of parts, unclean cleaning of parts after polishing, lubricating oil falling off equipment, debris from anode bags, water-based lubricants on plastic anode bags, uncured hanging film or coating, adhesives for special tapes, stabilizers in hydrogen peroxide, etc. Organic additives have a significant impact on certain properties of the coating, such as greatly reducing its protective


